Overloaded Operations and Conversions
重载运算符与类型转换
基本概念
- 除了重载的函数调用运算符
operator()外,重载的运算符不能有默认实参。 - 如果一个运算符函数是成员函数,第一个(左侧)操作数绑定到隐式的
this指针上。 对于一个运算符函数来说,它或者是类的成员,或者至少含有一个类类型的参数:
1
2// error: cannot redefine the built-in operator for ints
int operator+(int, int);可被重载与不可被重载的运算符:

- 对于既可以是一元又可以是二元的运算符(+,-,*和&),定义的运算符取决于参数的数量。
重载的运算符具有和内置运算符相同的优先级和结合律。
可以像调用普通函数一样调用重载运算符函数:
1
2
3// equivalent calls to a nonmember operator function
data1 + data2; // normal expression
operator+(data1, data2); // equivalent function call部分运算符保证了运算对象求值的顺序,但使用重载的运算符函数实际上是函数调用,不能保证运算对象的求值顺序。
输入和输出运算符
- 输入运算符必须处理输入出错的情况,但输出运算符不需要。
算术与关系运算符
- 当一个类同时重载了算术运算符和对应的复合赋值运算符时,使用复合赋值运算符来定义算术运算符效率更高:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8// assumes that both objects refer to the same book
Sales_data
operator+(const Sales_data &lhs, const Sales_data &rhs)
{
Sales_data sum = lhs; // copy data members from lhs into sum
sum += rhs; // add rhs into sum
return sum;
}
赋值运算符
- 赋值运算符可以被重载,无论参数类型是什么,赋值运算符都应该被定义为成员函数。
下标运算符
递增与递减运算符
- 后置的递增与递减运算符接收一个额外(不被使用)的
int类型参数,用于区分前置版本:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10class StrBlobPtr {
public:
// increment and decrement
StrBlobPtr& operator++(); // prefix operators
StrBlobPtr& operator--();
StrBlobPtr operator++(int); // postfix operators
StrBlobPtr operator--(int);
// other members as before
};
成员访问运算符
根据
point类型的不同,point->mem分别等价于(*point).mem; // (1) point is a built-in pointer typepoint.operator->()->mem; // (2) point is an object of class type
如果
point是指针,point->mem等价于(1);如果point是定义了operator->()的类的一个对象,则使用point.operator->()的结果来获取mem,若该结果是一个指针,则执行(1),若该结果为定义了operator->()的类的一个对象,则重复调用当前步骤。
函数调用运算符
标准库函数对象
- 以下类型定义在
functional头文件中
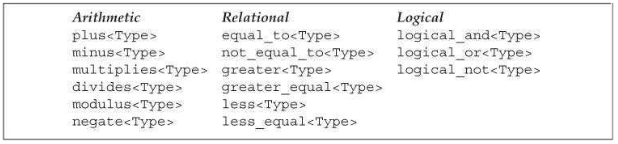
- 内置关系运算符
<对于指针类型是未定义的,但标准库提供的函数对象保证了对指针类型是正确定义的:1
2
3
4
5vector<string *> nameTable; // vector of pointers
// error: the pointers in nameTable are unrelated, so < is undefined
sort(nameTable.begin(), nameTable.end(), [](string *a, string *b) { return a < b; });
// ok: library guarantees that less on pointer types is well defined
sort(nameTable.begin(), nameTable.end(), less<string*>());
可调用对象与function
调用形式(call signature)指明了调用返回的类型以及传递给调用的实参类型。例如:
1
int (int, int)具有相同调用形式的可调用对象可能具有不同的类型,标准库
function类型可以存放具有相同调用形式的可调用对象。以下是function的操作: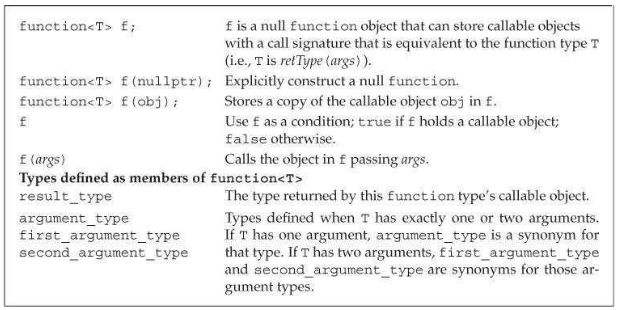
重载、类型转换与运算符
- 转换构造函数和类型转换运算符共同定义了类类型转换(class-type conversions),这样的转换有时也被称作用户定义的类型转换(user-defined conversions)。
类型转换运算符(conversion operator)是类的一种特殊成员函数,它的形式如下:
1
operator type() const;编译器一般不会将声明为
explicit的类型转换运算符用于隐式类型转换:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9class SmallInt {
public:
// the compiler won't automatically apply this conversion
explicit operator int() const { return val; }
// other members as before
};
SmallInt si = 3; // ok: the SmallInt constructor is not explicit
si + 3; // error: implicit is conversion required, but operator int is explicit
static_cast<int>(si) + 3; // ok: explicitly request the conversion有一个例外,在表达式用于条件判断时,声明为
explicit的类型转换会隐式地执行。
本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-SA 4.0 协议 ,转载请注明出处!