Strings, Vectors, and Arrays
string类型
string的定义与声明
- 初始化
string的方法

- 当我们使用
=初始化一个变量时,编译器将=右边对象的内容复制到新创建的对象,以进行拷贝初始化。当我们省略=时,进行的是直接初始化。
string上的操作
- string的size方法返回一个
string::size_type类型的值,该类型是unsigned类型。 - 可以将字符字面量和字符串字面量转化为
string,将string与字符或字符串字面量拼接时,时+运算符的操作数必须至少有一个为string类型。1
2string s1 = "hello", s2 = "world";
string s3 = s1 + ", " + s2 + '\n';
处理string中的字符
- 定义在
cname头文件中的名字在std命名空间中,而定义在.h头文件中的名字则不在std命名空间中。 在以下range
for的每一次迭代中,declaration中的变量由expression中下一元素的值初始化。1
2for (declaration : expression)
statement若要在range
for中改变expression中元素的值,则需要在declaration中将变量定义为引用类型。1
2
3
4string s("Hello World!!!"); // convert s to uppercase
for (auto &c : s) // for every char in s (note: c is a reference)
c = toupper(c); // c is a reference, so the assignment changes the char in s
cout << s << endl; // HELLO WORLD!!!
vector类型
vector的定义与声明
- 初始化
vector的方法
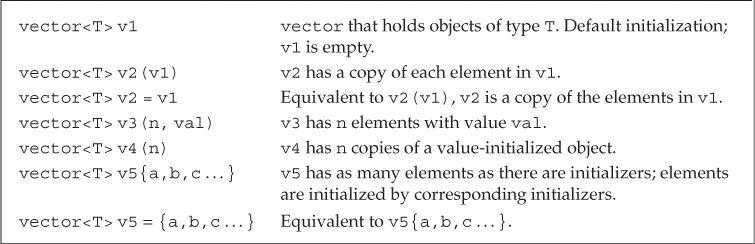
若
vector中的元素为内置类型(例如int),则vector中元素会被初始化为0;若vector中的元素为class类型(例如string),则vector中元素会进行该元素的默认初始化。1
2vector<int> ivec(10); // ten elements, each initialized to 0
vector<string> svec(10); // ten elements, each an empty string对于必需显式初始化的对象,由于没有默认初始化方法,创建该类型的
vector时,不能只提供size一个参数。- 如果无法进行列初始化,编译器会从根据给定的值寻找其他适合的方法进行初始化。
1
2
3
4vector<string> v5{"hi"}; // list initialization: v5 has one element
vector<string> v6("hi"); // error: can't construct a vector from a string literal
vector<string> v7{10}; // v7 has ten default-initialized elements
vector<string> v8{10, "hi"}; // v8 has ten elements with value "hi"
向vector添加元素
- 如果循环体中向
vector添加了元素,则不能使用rangefor。
vector的其他操作
vector(以及string)的下标运算符只能获取已有的元素,不能添加新的元素。
迭代器(iterators)简介
- 若容器是空的,则
begin返回与end相同的迭代器。 - 大多数迭代器没有
<运算符,所以通常在迭代器比较时使用!=。 cbegin和cend返回const_iterator的迭代器,不能修改指向的对象。
数组
数组的声明与初始化
- 数组的维度必须是常量表达式
1
2
3
4
5
6unsigned cnt = 42; // not a constant expression
constexpr unsigned sz = 42; // constant expression
int arr[10]; // array of ten ints
int *parr[sz]; // array of 42 pointers to int
string bad[cnt]; // error: cnt is not a constant expression
string strs[get_size()]; // ok if get_size is constexpr, error otherwise - 复杂的数组声明
1
2
3
4int *ptrs[10]; // ptrs is an array of ten pointers to int
int &refs[10] = /* ? */; // error: no arrays of references
int (*Parray)[10] = &arr; // Parray points to an array of ten ints
int (&arrRef)[10] = arr; // arrRef refers to an array of ten ints
指针与数组
decltype(ia)返回的是数组类型1
2
3
4
5int ia[] = {0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9}; // ia is an array of ten ints
auto ia2(ia); // ia2 is an int* that points to the first element in ia
ia2 = 42; // error: ia2 is a pointer, and we can't assign an int to a pointer
auto ia2(&ia[0]); // now it's clear that ia2 has type int*
decltype(ia) ia3 = {0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9}; // ia3 is an array of ten intsiterator头文件提供了begin与end,分别返回数组的首地址与数组最后一个元素后一位置的地址。1
2
3int ia[] = {0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9}; // ia is an array of ten ints
int *beg = begin(ia); // pointer to the first element in ia
int *last = end(ia); // pointer one past the last element in ia
指针运算
- 库类型强制要求下标必须为
unsigned类型,原始数组无此要求。1
2
3int ia[] = {0,2,4,6,8}; // array with 5 elements of type int
int *p = &ia[2]; // p points to the element indexed by 2
int k = p[-2]; // p[-2] is the same element as ia[0]
与旧代码的接口
string类型的c_str成员函数的返回值可用于初始化C风格字符串,该返回值类型为const char*。1
2
3string s("Hello world"); // s holds Hello World
char *str = s; // error: can't initialize a char* from a string
const char *str = s.c_str(); // ok
多维数组
- 对多维数组使用range
for时,除最内层循环之外的循环控制变量必须为引用类型。
本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-SA 4.0 协议 ,转载请注明出处!